It determines the orientation of the orbital in space relative to the other orbitals in the atom. How many possible orbitals are there when n 3 l 1 and m l 0.

S P D F Orbitals Explained 4 Quantum Numbers Electron Configuration Orbital Diagrams Youtube
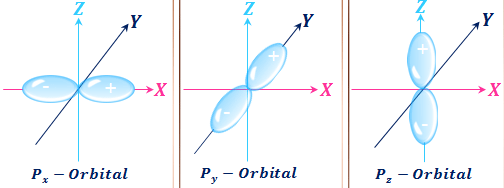
Orbital Angular Momentum Quantum Number L.

How to determine quantum numbers from orbital diagrams. L describes the shape of the orbital. With these quantum numbers set the number of possible orbitals equal to one. The energy of an electron in an orbital with quantum number nfor an atom with atomic number Zis given by.
Use the periodic table below to keep track of where the s p and d blocks are located. Using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes lines or circles as shown below 1s. From solving the SE.
Quantum Numbers Atomic Orbitals and Electron Configurations - YouTube. Electron configurations partial orbital diagrams showing valence electrons only and number of inner electrons for the following elements. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers.
N 1 2 3 8. Z 43 c lead Pb. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the four quantum numbers.
The Aufbau principle the Pau. Shape of orbital L 0 1 2 3 n-1 Magnetic Quantum Number m L. Z 19 b technetium Tc.
L 0 - m_l 0 orbital s l 1 - m_l -101 orbital p l 2 - m_l -2-1012 orbital d l 3 - m_l -3-2-10123 orbital f and so on. This video shows you how to identify or determine the 4 quantum numbers n l ml and ms from an element or valence. Spin quantum number ms ½ or -½.
The Orbital Angular Momentum Quantum Number l The orbital angular momentum quantum number l determines the shape of an orbital and therefore the angular distribution. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules. The allowed values of n are therefore 1 2 3 4.
The magnetic quantum number m can be any integer between -l and l. Z 82 PLAN. 72 Orbital Energies in Single and Multielectron Species The relationship between the principal quantum number n and orbital energy is shown in an orbital energy diagram Figure 721.
For more information about angular nodes see Electronic Orbitals. Electron orbital diagrams are a way of illustrating what energy level and orbital shape of the probable location of each of the electrons of an element. Figure 721 Identify Orbital Energies in Single-Electron Species Orbital energies n 1 to n 4 in a singleelectron species.
Orientation m L interval of - L L. The principal quantum number of electrons in the F-block is period minus 2. L 4 5 6 skipping j although orbitals of these types are rarely required56 The electron configurations of molecules are written in a similar way except that molecular orbital labels.
E n. Which orbital is filled after 6s. It also shows you how to draw the atomic orbital diagrams and the orbital energy levels of an atom.
For hydrogen-like atoms one finds that electrons in many-electron. After f the sequence continues alphabetically g h i. 0 1 2 3.
As the symbol suggests it has to do with l the angular momentum quantum number. One of the electrons in an orbital is arbitrarily assigned an s quantum number of 12 the other is assigned an s quantum number of -12. Specifies which orbital within a sublevel you are likely to find the electron.
It discusses how the energy levels and sublevels of electrons suc. The number of angular nodes is equal to the value of the angular momentum quantum number l. There is a simple way of remembering how electrons fill up orbitals shown in the accompanying diagrams.
Magnetic quantum number mℓ-2 -1 0 1 2. The atomic number gives the number of electrons and the periodic table shows the order for filling orbitals. The principal quantum number of electrons in the D-block is period minus 1.
The first three n l m l specify the particular orbital of interest and the fourth m s specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. Electron configurations and orbital diagrams can be determined by applying the Pauli exclusion principle no two electrons can have the same set of four quantum numbers and Hunds rule whenever possible electrons retain unpaired spins in degenerate orbitals. Numbers of possible orbitals when principle quantum number equal to four 1 4s 3 4p 5 4d 7 4f 16.
This quantum number has values from -ℓ through zero to ℓ. This chemistry video tutorial explains the 4 quantum numbers n l ml and ms and how it relates to the electron configuration of an element. Lets look at various values of l and their corresponding m_l.
The three quantum numbers n l and m that describe an orbital are integers. A box line or circle is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. 1 s 2 p 3 d and 4 f for the orbital and the superscript number tells you how many electrons are in that orbital.
Modern usage indicates orbitals with an azimuthal quantum number l of 0 1 2 or 3 respectively. Thus it takes three quantum numbers to define an orbital but four quantum numbers to identify one of the electrons that can occupy the orbital. Principal Quantum Number n.
Orbital diagrams use the same basic format but instead of numbers for the electrons they use and arrows as well. It explains the sublevels s p d and f. Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom.
What is an electron orbital diagram. 6d 1s 2s 3s. This video provides 3 example practic.
The principal quantum number n cannot be zero. The first number is the principal quantum number n and the letter represents the value of l angular momentum quantum number. The angular quantum number l can be any integer between 0 and n - 1.
An orbital diagram or orbital box diagram is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. If n 3 l can be either 0 1 or 2.

Distribution Of Electrons Quantum Numbers Mcc Organic Chemistry
Quantum Number Orbital Definition Formula Diagram Shape

Quantum Numbers The Easy Way Youtube

Quantum Numbers The Easy Way Youtube
